01/29/2016 Update
I created a React component based on this article.
Background
To be honest, not many people are willing to toss with the scroll bar in browsers.
The first and the most critical issue is about the compatibility: to start with, Firefox (at least before 5.0) doesn’t support any CSS styling for scrollbar.
Secondly, most browsers will use their OS default scrollbar styles. Hence it seems no reason for developers to change the styles.
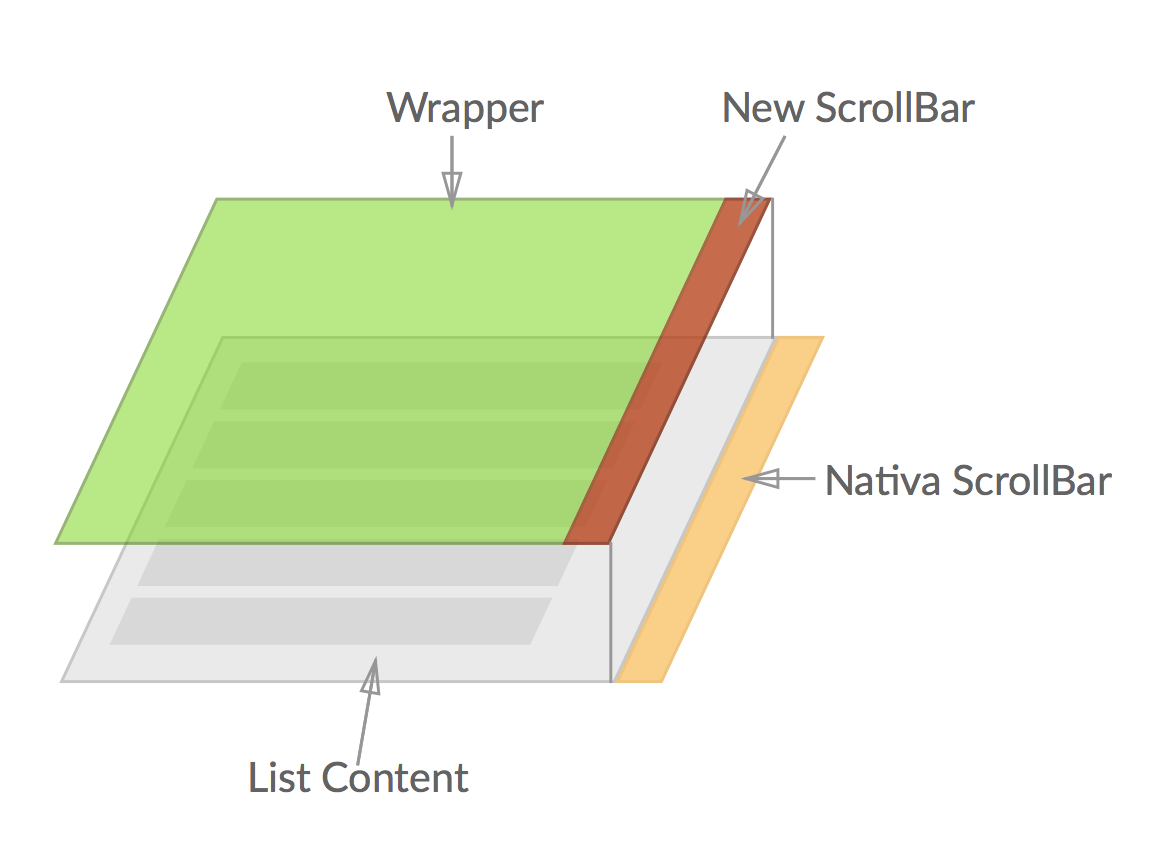
However, there are three list columns in one of my latest projects. In OS X, the scrollbar will always show if the user is using a mouse, taking a space of 18px width, which causes serious damage to the entire page. As the figure shows below:

Think
The default scrollbar of OS X is completely different when using the touchpad and the mouse. When using a touchpad, the scrollbar’s position is absolute in related to the document, and will hide itself if the user not scrolls it. When using a mouse, to save the user’s time of finding the scrollbar, it will be always shown there.
I am thinking to create a third party scrollbar and take the control of the div, and it would be better if it is wrapped as a React component, so that I can reuse it anytime anywhere.
Build
The component will be like this:
To use:
import ScrollView from 'ScrollView.jsx`;
...
render() {
return (
<ScrollView>
{aListThatScrolls}
</ScrollView>
);
}
import React from 'react';
import Styles from './ScrollView.less';
export default React.createClass({
getInitialState() {
return {
height: 0,
handlerScrollTop: 0,
handlerHide: true
};
},
handlerHider: null,
scrollHandler: null,
lastPos: 0,
componentDidMount() {
window.addEventListener('resize', this.handleResize);
document.addEventListener('mousemove', this.handleHandlerMouseMove);
document.addEventListener('mouseup', this.handleHandlerMouseUp);
this.updateHeight();
},
componentWillUnmount() {
window.removeEventListener('resize', this.removeResize);
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', this.handleHandlerMouseMove);
document.removeEventListener('mouseup', this.handleHandlerMouseUp);
},
render() {
return (
<div className="ScrollView">
<div className="scrollbar">
<div className={"handler " + (this.state.handlerHide ? 'hide' : '')}
style=
onMouseDown={this.handleHandlerMouseDown}/>
</div>
<div className="scroller" onScroll={this.handleScroll} ref="scroller">
{this.props.children}
</div>
</div>
);
},
handleScroll(e) {
clearTimeout(this.handlerHider);
let pos = e.target.scrollTop / (e.target.scrollHeight- this.state.height) * 0.8;
this.setState({
handlerScrollTop: pos * 100,
handlerHide: false
}, () => {
this.handlerHider = setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({handlerHide: true});
}, 1500);
});
if (pos < 0.2 && pos < this.lastPos && this.props.onApproachingTop) {
this.props.onApproachingTop();
}
if (pos > 0.6 && pos > this.lastPos && this.props.onApproachingBottom) {
this.props.onApproachingBottom();
}
this.lastPos = pos;
},
handleResize() {
this.updateHeight();
},
handleHandlerMouseDown(e) {
this.scrollHandler = e.target;
clearTimeout(this.handlerHider);
this.setState({handlerHide: false});
},
handleHandlerMouseMove(e) {
if (this.scrollHandler) {
let pos = (e.pageY) / this.state.height;
pos = (pos < 0 ? 0 : (pos > 0.8 ? 0.8 : pos)) * 100;
React.findDOMNode(this.refs.scroller).scrollTop = pos * React.findDOMNode(this.refs.scroller).scrollHeight / 100;
}
},
handleHandlerMouseUp(e) {
this.scrollHandler = null;
clearTimeout(this.handlerHider);
this.handlerHider = setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({handlerHide: true});
}, 1500);
},
updateHeight() {
this.setState({height: React.findDOMNode(this).offsetHeight});
}
});
@import (reference) "../Base/Base.less";
.ScrollView {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100%;
position: relative;
.scrollbar {
position: absolute;
width: 8px;
top: 0;
right: 0;
height: 100%;
.handler {
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
position: absolute;
width: 6px;
left: 1px;
border-radius: 3px;
z-index: 1;
.transition(@time: 0.2s, @type: background-color);
&.hide {
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
&:hover {
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
}
&:active,
&:focus {
cursor: default;
}
}
}
.scroller {
overflow-y: auto;
height: 100%;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: -20px;
padding-right: 20px;
}
}
Something highlighted:
- The principle of the component if not to destroy the scrollbar, but wrapping the scrollable div using a CSS attribute:
overflow: hidden, and make the scrollable div a little bit wider than the wrapper. Then by hiding the native scrollbar, we can create a artificial scrollbar usingposition: absolute.
- Also, the height of the scrollbar’s thumb is set to 20% of the document’s height, so the maximum distance between the top of the page and the top of the thumb is 80%. To calculate the position of the thumb, we use
let pos = e.target.scrollTop / (e.target.scrollHeight- this.state.height) * 0.8; - Finally, to make the thumb clickable, three events are used: mouseDown, mouseUp, and mouseMove.
For a ready-to-use React component, go to my github. Or $ npm install --save-dev react-free-scrollbar.